Harmful algal blooms (HABs) are a serious marine environmental problem where rapid growth of toxin-producing phytoplankton leads to massive death of cultured fish and natural marine resources, resulting in devastating damage to fishery. In CEARAC’s HAB activities, following two phenomena are included:
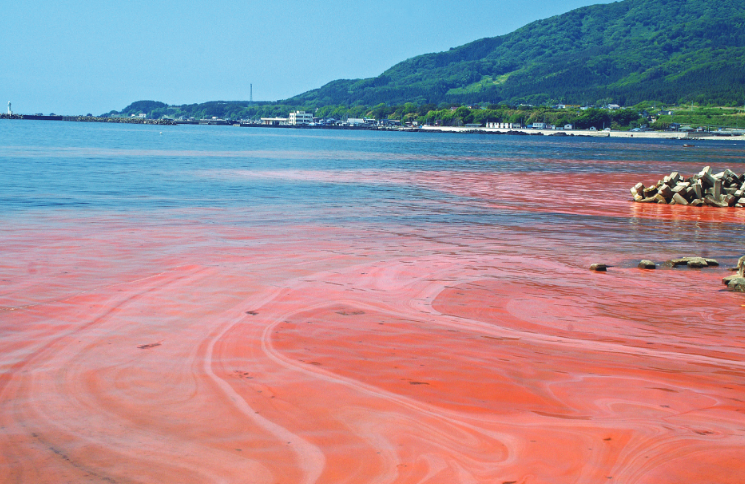
・Red Tide: Water discoloration by increased phytoplankton
・Shellfish Toxin: Shellfish poisoning by feeding toxin-producing phytoplankton
Same as land-based plants, phytoplankton needs sunlight and nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus). When rainwater increases in the rainy season or by typhoons, large amounts of nutrients run into the sea water through rivers. Then when other conditions such as sunlight and water temperature are met, phytoplankton grows rapidly. As long as the phytoplankton is feed for fish, no problem happens. However, if toxic plankton grows, it may cause extensive damage.
Sea Surface Temperature is increasing by global warming, and because of this, marine organisms which are native in the southern waters are often seen in the NOWPAP region at present. Actually, in some cases, damages are caused by different species from the past ones. Therefore, it is important for CEARAC to collect and share information of HABs that occurred in respective NOWPAP member states for them to design effective countermeasures.
CEARAC Activity
CEARAC developed “HAB Integrated Website” as a useful HAB-related information resource. The website has information on HAB occurrences in the NOWPAP member states and includes “Cochlodinium Homepage” to introduce Cochlodinium polykrokoides, one of the major HAB species in the NOWPAP region, “HAB Reference Database.” All the CEARAC publications on HABs such as “Booklet of Countermeasures against Harmful Algal Blooms in the NOWPAP region” are also available.
・Case Study Reports on Harmful Algal Blooms(HABs) in the NOWPAP Region (2008-2011)
・Booklet of Countermeasures against Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs) in the NOWPAP Region (2007)
・Cochlodinium Pamphlets (2007)
・Integrated Report on Harmful Algal Blooms for the NOWPAP Region (2005)
・National Reports on Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs) in the NOWPAP Region (2004-2005)
・Summaries of National Reports on Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs) (2004-2005)
It features various information related to HABs, including publications, databases, and species of HABs that are pbroblematic in the NOWPAP region.
Detailed information about the biology and ecology of Cochlodinium, the red tides it causes, and measures to deal with them is provided.
The database can be searched through several methods. Please refer to the instructions on the search method provided on the site.